
Variables are sometimes known as fields or properties. Tied to a class or object (static and instance variables). Similarly, Dart supports top-level variables, as well as variables Or-if you must defer type checking until runtime-theĭart supports generic types, like List (a list of integers)ĭart supports top-level functions (such as main()), as well asįunctions tied to a class or object ( static and instance That any type is allowed, use the type Object? You can add ! to assert that it isn’t nullĪn example: int x = nullableButNotNullInt! If you know that an expression never evaluates to null Putting a question mark ( ?) at the end of its type.įor example, a variable of type int? might be an integer, Variables can’t contain null unless you say they can. Using null safety requires a language version of at least 2.12.Īlthough Dart is strongly typed, type annotations are optionalīecause Dart can infer types. Version note: Null safety was introduced in Dart 2.12. With the exception of null (if you enable sound null safety),Īll objects inherit from the Object class.
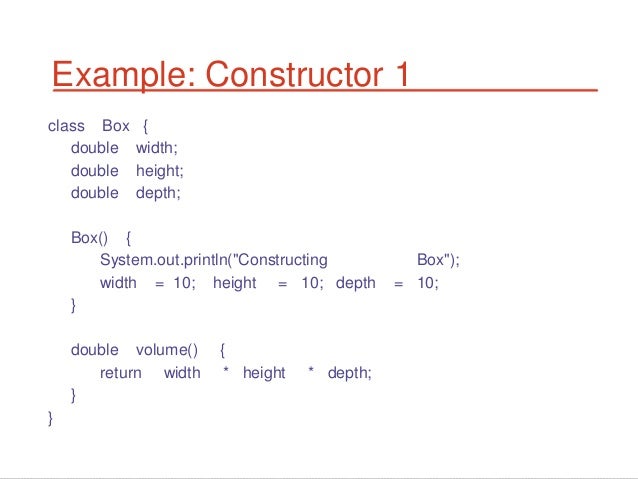
CONSTRUCTOR DEFINITION CODE
This site’s code follows the conventions in theĪs you learn about the Dart language, keep these facts and concepts inĮverything you can place in a variable is an object, and every Is determined by its initial value ( 42). var A way to declare a variable without specifying its type. main() The special, required, top-level function where app execution $ variableName (or $) String interpolation: including a variable or expression’s stringĮquivalent inside of a string literal.

Number literals are a kind of compile-time constant. int Another type, indicating an integer.Īre String, List, and bool. void A special type that indicates a value that’s never used.įunctions like printInteger() and main() that don’t explicitly return a value
A single-line comment.ĭart also supports multi-line and document comments.įor details, see Comments. Here’s what this program uses that applies to all (or almost all) DartĪpps: // This is a comment. Var number = 42 // Declare and initialize a variable. This is where the app starts executing. Print('The number is $aNumber.') // Print to console. The following code uses many of Dart’s most basic features: If you see empty boxes instead of DartPads, go to theĭartPad troubleshooting page. This page uses embedded DartPads to display some of the examples. You can play with most of Dart’s language features using DartPad Whenever you want more details about a language feature, To learn more about Dart’s core libraries, see the
CONSTRUCTOR DEFINITION HOW TO
That you already know how to program in another language.įor a briefer, less complete introduction to the language, see the Variables and operators to classes and libraries, with the assumption This page shows you how to use each major Dart feature, from Generic collections and the types they contain.Using parameterized types with constructors.Let’s assume we have following code in Employee class. This is the way java runtime distinguish between a normal method and a constructor. If we add a return type to a constructor, then it will become a method of the class. Since constructor can only return the object to class, it’s implicitly done by java runtime and we are not supposed to add a return type to it. Whenever we use new keyword to create an instance of a class, the constructor is invoked and the object of the class is returned. Sometimes constructors are also referred to as special methods to initialize an object. Constructors are almost similar to methods except for two things - its name is the same as the class name and it has no return type. Constructor in java is used to create the instance of the class.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
